■ 이론
JAVA 에서 중요한 2가지
컬렉션과 JDBC
1. Collection : 자바의 자료구조
- 무한한 데이터의 집합
1) Set - HashSet, TreeSet
Set의 특징 : 순서 X, 동일데이터 X
2) Map
key, value
주요 클래스 : Hashtable, HashMap,
Hashtable 멀티스레드 지원, 웹
HashMap, 멀티스레드 지원 x, 자바에서는 HashMap이 좀더 빠르긴 함.
3) List - ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector
ArrayList는 맨 마지막만 비워두고 쭉 당겨지는 구조.
데이터 수정할 때는 ArrayList가 편하다.
웹에서는 무조건 ArrayList
Vector : 유산클래스
Set, Map, List는 인터페이스
인터페이스를 만드는 이유,
형식을 미리 지정해놓을 수 있다. 인터페이스는 설계도다.
미리 설계를 해놓고, 설계를 확장한다.
여기엔 추상화, 다형성 개념이 다 들어간다.
A ap = new A(); new라는 연산자를 사용해야 heap에 저장할 수 있다.
ap.a = 100;
System.out.println(bp.a);
A ap = new A();
System.out.println(ap);는 System.out.println(ap.toString());이 생략되어 있다.
■ Test01.java - List 와 Iterator
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); // 뒤에 제너릭은 안 써도 된다.
List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>(); // 다형성과, 인터페이스의 특징
list.add("유재석"); // 데이터 삽입
list.add("하하");
list.add("김종국");
list.add("전소민");
// add만 하면 알아서 데이터가 들어간다. -> 프레임워크
// generic : 들어갈 데이터의 타입을 지정
String[] name2 = new String[list.size()];
list.toArray(name2); // 해당 자료형을 배열로 바꿔준다.
for(int i=0; i<name2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(name2[i]);
}
System.out.println("-----");
list.remove(1); // 데이터 삭제(위치를 이용하여 지우기)
list.remove("전소민"); // 데이터 삭제(객체를 이용하여 지우기)
// 1. 확장 for문
for(String name : list) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("-----");
// 2. 전통적인 for문
for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) { // size : 데이터 크기
String name = list.get(i); // 해당하는 데이터 꺼내기
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("-----");
// 3. Itertator
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); // 반복자, 순서가 없는 데이터를 출력할 때 특히 유용
while(it.hasNext()) {
String name = it.next();
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("-----");
if(list.contains("유재석")) { // 찾기
System.out.println("유재석은 저희 멤버!");
} else {
System.out.println("유재석은 멤버가 아님!");
}
list.clear(); // 데이터 모두 지우기
}
}
■ Test02.java - Hashtable과 Enumeration
import java.util.*;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable<String, String> ht = new Hashtable<>();
ht.put("유재석", "개그맨"); // 데이터 삽입(키와 값으로 넣어준다.)
ht.put("류현진", "야구선수");
ht.put("손흥민", "축구선수");
// for문을 사용한다면.
for(Enumeration<String> enu = ht.keys(); enu.hasMoreElements();) {
String key = enu.nextElement();
System.out.println(key + "님의 직업은 " + ht.get(key) + "입니다.");
}
Enumeration<String> enu = ht.keys();
// 모든 키를 Enumeration 반복자로 반환
while(enu.hasMoreElements()) {// hasNext 와 동일한
String key = enu.nextElement();
System.out.println(key + "님의 직업은 " + ht.get(key) + "입니다.");
// 순서대로 나오진 않지만 전체 출력을 보장한다.
// 순서가 없기 때문에 for문을 사용할 수 없다. for문을 사용하려면 index가 있어야 한다.
}
/*
* // ht.remove("손흥민"); // 데이터 삭제(키)
* // ht.clear(); // 모든데이터 삭제
*
* if(ht.containsKey("손흥민")) { // 데이터 찾기 - 키가 존재하면 true, 아니면 false
* System.out.println("손흥민님의 직업은 " + ht.get("손흥민") + "입니다"); // 키로 해당 데이터 꺼내기 }
* else { System.out.println("손흥민은 저희 회원이 아닙니다."); }
*/
}
}
■ Test03 - File
import java.io.*;
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava\\aaa.txt"); // 추상적인 경로
File file2 = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava", "aaa.txt");
File dir = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava");
File file3 = new File(dir, "aaa.txt");
// file, file2, file3은 모두 같은 위치를 가르킨다.
// 근데 리눅스에서는 역슬래쉬가 아니라 온슬래쉬를 구분자로 사용한다.
File file4 = new File("C" + File.separator + "myProject" + File.separator
+ "myJava" + File.separator + "testJava" + File.separator + "aaa.txt");
/*
System.out.println("File.separator = " + File.separator);
System.out.println("File.separatorChar = " + File.separatorChar);
System.out.println("File.pathseparator = " + File.pathSeparator);
System.out.println("File.pathseparatorChar = " + File.pathSeparatorChar);
*/
}
}
■ Test04 - File2
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File dir = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava");
File file = new File(dir, "aaa.txt");
if(file.createNewFile()) { // 파일이 없으면 만들고 true, 있으면 false 반환
System.out.println("aaa.txt 파일을 만들었습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("aaa.txt 파일은 이미 존재합니다.");
}
// file.delete(); // 파일 삭제
file.deleteOnExit(); // 프로그램 종료시 삭제, delete() 메소드는 즉시 삭제
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
■ Test05.java - FileOutputStream
import java.io.*;
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File dir = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava");
File file = new File(dir, "aaa.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true);
// 1byte를 파일로 보낼 때 사용하는 클래스 : FileOutputStream
// 생성자 2번째 매개변수가 true면 append, false면 rewrite,default는 false
String msg = "Hello, Java!";
byte[] by = msg.getBytes();
fos.write(by, 7, 4); // 전송데이터, 시작위치, 시작부터 전송할 갯수.
// fos.write(by) // by 배열의 모든 데이터 전송
/*
fos.write('A'); // byte 단위로 전송이 된다.
fos.write(66);
*/
}
}
■ Test06.java - FileInputStream
import java.io.*;
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File dir = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava");
File file = new File(dir, "aaa.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
while(true) {
int res = fis.read(); // 한글자씩 읽어서 반환(ASC 코드값으로 반환이 된다.)
if(res == -1) break; // 읽은 값이 -1이면 파일을 끝을 의미함 (EOF))
System.out.println((char)res);
}
}
}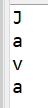
■ Test07.java - BufferedOutputStream / DataOutputStream
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test07 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File dir = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava");
File file = new File(dir, "bbb.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(bos);
int a = 10;
double b = 10.23;
String msg = "Hello";
dos.writeInt(a);
dos.writeDouble(b);
dos.writeUTF(msg);
// dos.flush();
dos.close(); // close 메소드는 flush()를 먼저 실행 후 닫는다.
}
}
■ Test08.java - BufferedInputStream / DataInputStream
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File dir = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava");
File file = new File(dir, "bbb.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bis);
int a = dis.readInt();
double b = dis.readDouble();
String msg = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
■ Test09.java - File/Buffered/Print Writer
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Test09 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File dir = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava");
File file = new File(dir, "ccc.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(bw);
pw.println("안녕하세요!");
pw.println(20);
pw.close();
}
}
■ Test10.java - File/Buffered Reader
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File dir = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava");
File file = new File(dir, "ccc.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
while(true) {
String msg = br.readLine();
if(msg == null) break; // 문자열에서 파일의 끝은 null이다.(EOF 값이 null)
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
}
■ Test11.java - Serializable
import java.io.*;
class A11 implements Serializable{// 객체의 직렬화, 역직렬화 implements Serializable만 해주면 알아서 해준다.
// 어딘가로 보낼 때.
int a = 10;
transient int b = 20; // 네트워크 같은 곳에 전송할 때 이 값은 전송 안 하겠습니다.
int c = 30;
}
public class Test11 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File dir = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava");
File file = new File(dir, "ddd.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
A11 ap = new A11();
ap.a = 100;
ap.b = 200;
ap.c = 300;
oos.writeObject(ap);
oos.close(); // java.io.NotSerializableException : 직렬화가 이뤄지지 않아서 발생
}
}
■ Test12.java
import java.io.*;
public class Test12 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
File dir = new File("C:\\myProject\\myJAVA\\testJava");
File file = new File(dir, "ddd.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
Object obj = ois.readObject(); // 만약 해당하는 클래스가 없다면? ClassNotFoundException 발생
A11 ap = (A11)obj; // 자식이 부모의 객체로 만들어질 수 있다.
System.out.println(ap.a);
System.out.println(ap.b);
System.out.println(ap.c);
}
}
'IT&코딩 > 자바 프로젝트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자바 프로젝트 6일차 - Servlet (testServlet) (0) | 2023.01.26 |
|---|---|
| 자바 프로젝트 5일차 - JSP 복습 3 (jspMember) (0) | 2023.01.24 |
| 자바 프로젝트 4일차 - JSP 복습 2 (jspBoard) (2) | 2023.01.22 |
| 자바 프로젝트 3일차 - JSP 복습 1 (2) | 2023.01.21 |
| 자바 프로젝트 2일차 - Java 복습2 (0) | 2023.01.21 |